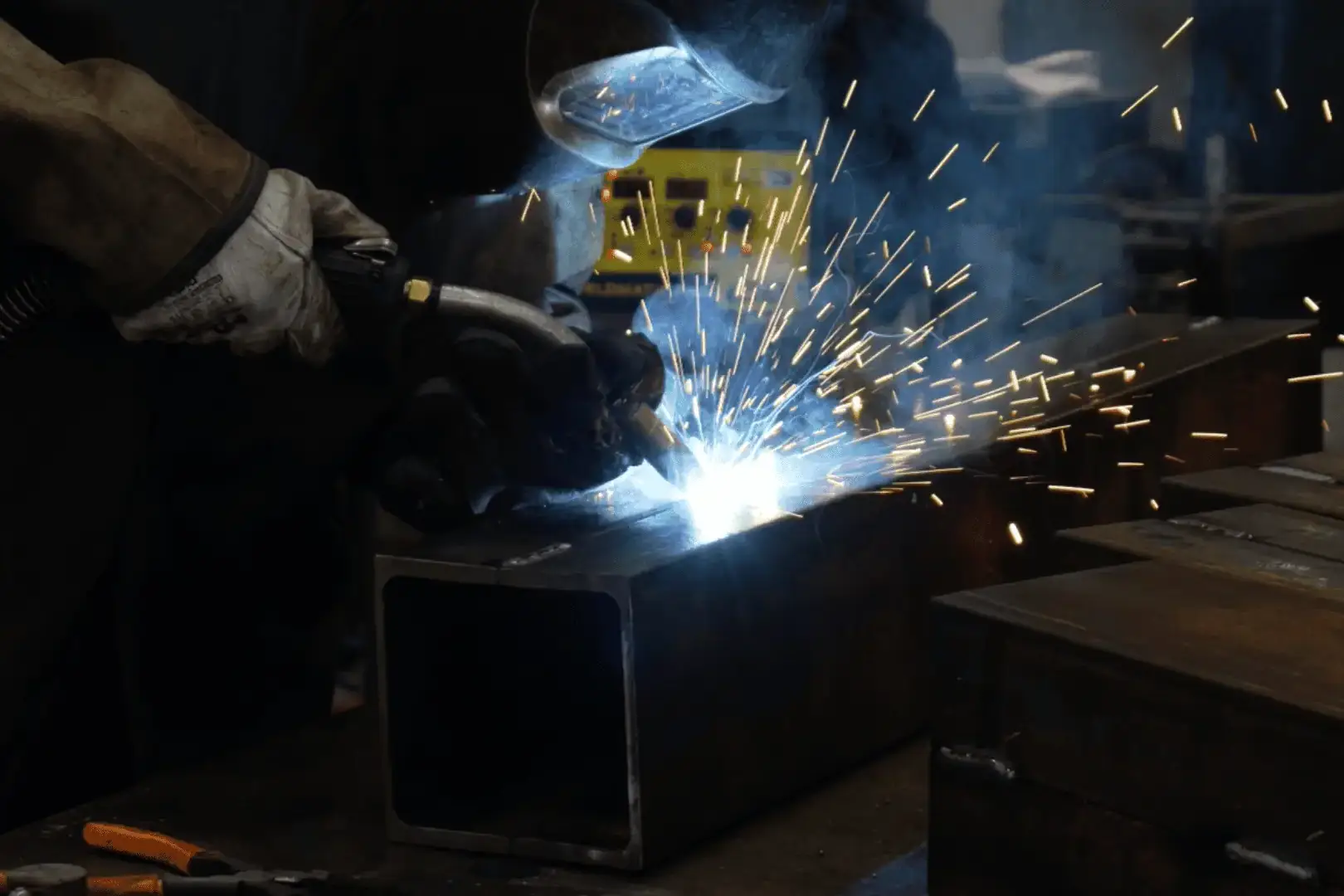
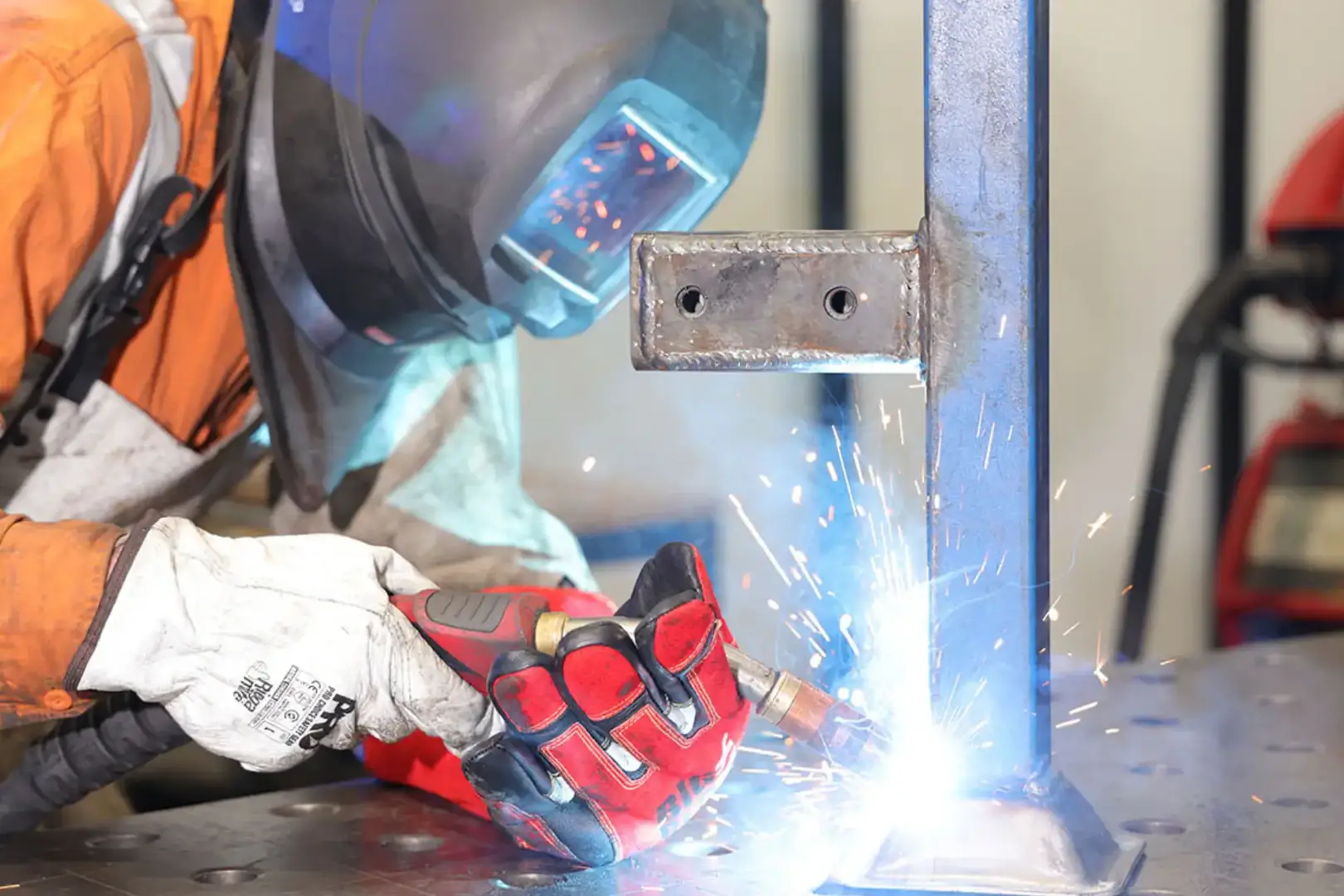
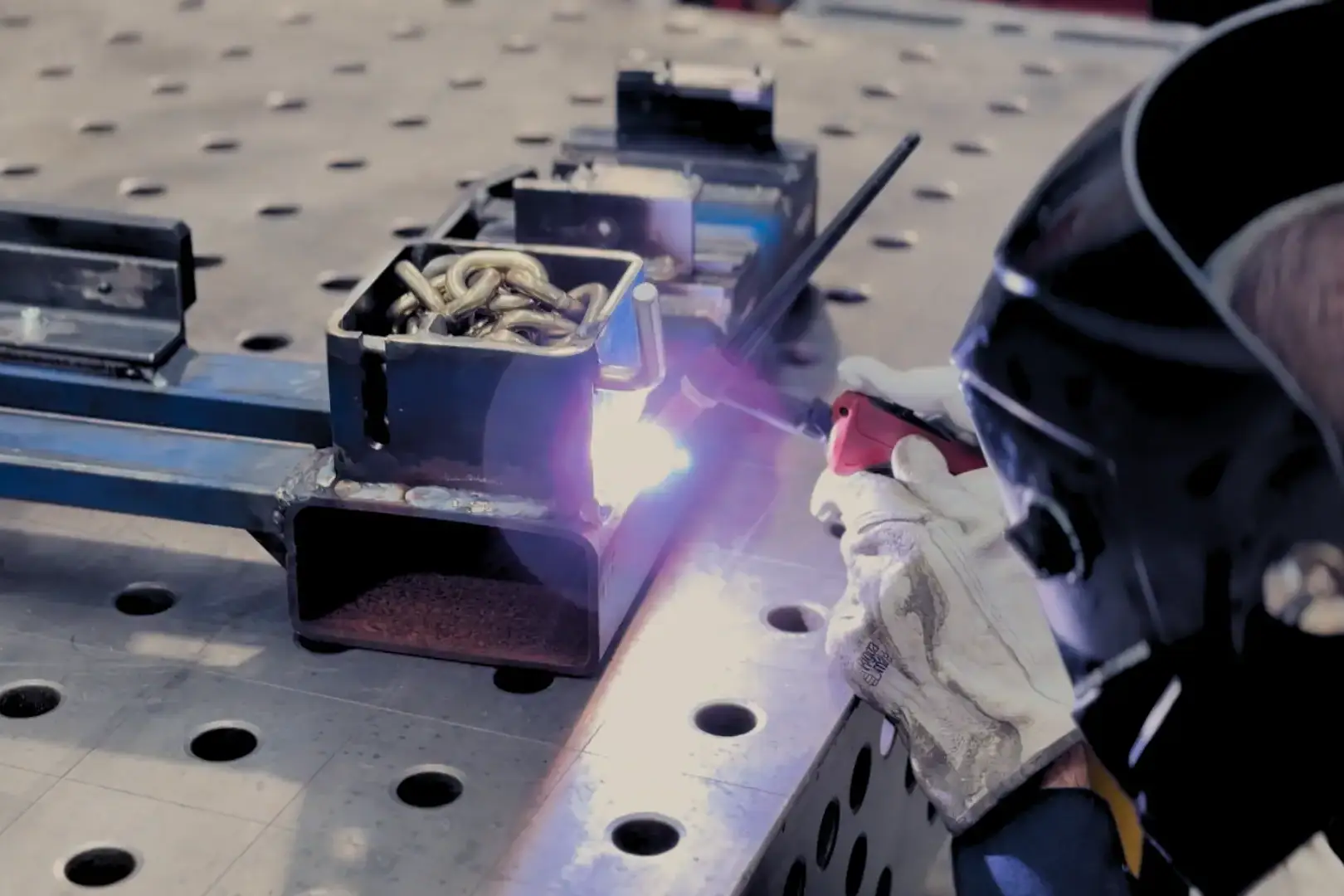
Spot welding is a common welding technique that plays a crucial role in metal fabrication, automotive manufacturing, and other industrial processes. It is a type of resistance welding where two or more metal sheets are joined together by applying pressure and heat generated from an electric current. Unlike traditional welding techniques, spot welding doesn’t require filler materials, gases, or flux. The process is highly efficient for joining thin metal sheets and is commonly used in large-scale production environments.
Spot welding is a reliable, cost-effective, and fast method to create strong joints, especially for metals like steel. It is most often used in industries where quick and efficient welding is necessary, such as automotive manufacturing, aerospace, and electronics. But how exactly does it work, and what are the key factors that make it so effective?
How Does Spot Welding Work?
Spot welding works by clamping metal sheets together and passing an electric current through the points where the sheets are touching. This electric current generates heat due to the resistance of the materials to the flow of electricity, causing the metals to melt and fuse together. As the metals cool down, a solid joint is formed.
This process is highly localised, meaning the heat generated is confined to the small area where the current passes through. As a result, the surrounding metal remains largely unaffected, reducing the risk of distortion or damage to the entire workpiece. Spot welding is typically used for welding materials that are thin, generally between 0.5 to 3 mm in thickness.
Spot Welding Process and Equipment
The equipment used in spot welding includes a welding machine equipped with electrodes made of copper or copper alloys. These electrodes are essential in delivering the current to the metal surfaces while also applying the necessary pressure to form the weld. The welding machine controls various parameters, including the duration of the current, the pressure applied by the electrodes, and the amount of current passing through the materials. If you don’t have access to the equipment Copamate delivers on spot welding services located in Campbellfield, Melbourne.
Step-by-Step Spot Welding Process:
- Preparation: The materials to be welded are cleaned to ensure there are no contaminants like rust, dirt, or oil, which could interfere with the weld quality.
- Positioning: The metal sheets are then aligned and clamped between the electrodes.
- Welding: Once everything is in place, the welding machine delivers a short burst of electric current. The duration of this current, typically between 0.01 and 0.63 seconds, depends on the material type and thickness. The heat generated melts the metal at the contact points.
- Cooling and Release: After the current is switched off, the electrodes remain clamped for a short time to allow the molten metal to cool and solidify, forming a strong bond between the sheets.
Materials Appropriate for Spot Welding
One of the major advantages of spot welding is its ability to join a wide variety of materials, although it works best with certain types of metals. The most common material used in spot welding is low-carbon steel due to its excellent electrical conductivity and ability to form strong welds. However, several other materials are suitable for spot welding.
Commonly Used Materials in Spot Welding:
- Low-carbon steel: Ideal for spot welding due to its low resistance to electric current, ensuring efficient heat generation and strong welds.
- Stainless steel: Can be spot welded but requires higher current and precise control due to its higher electrical resistance.
- Nickel alloys: Spot welding can also be used on nickel-based alloys, although they require more careful control of heat and pressure.
- Titanium: Requires high precision and careful monitoring of heat input to avoid damage to the metal’s properties.
Can Aluminium be Spot Welded?
Yes, aluminium can be spot welded, but it is more challenging than steel. This is due to aluminium’s higher thermal conductivity and lower electrical resistance. As a result, a higher current and more precise control of the welding parameters are required. If not properly managed, the weld can result in weak joints or excessive heat, leading to the deformation of the workpiece.
Moreover, aluminium forms an oxide layer on its surface, which can act as a barrier to welding. Therefore, it’s crucial to clean the surface of the aluminium before welding to ensure a strong bond. While spot welding aluminium is possible, other welding techniques like TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding are sometimes preferred for this material, especially for thicker pieces.
Can You Spot Weld Copper?
Copper, due to its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, is one of the most difficult metals to spot weld. Since copper conducts heat away from the weld site very quickly, it requires a much higher current than steel or aluminium to generate sufficient heat to form a weld. In addition, the welding electrodes can wear out quickly when welding copper because of the high heat.
Despite these challenges, spot welding copper is possible, especially in industries where copper is a critical material, such as in electrical components. Achieving a successful weld often requires specialised equipment and advanced techniques.
How Many Amps to Spot Weld 18650?
18650 batteries, commonly used in electric vehicles, laptops, and other electronics, require precise spot welding during assembly. The amperage required to spot weld 18650 battery cells depends on several factors, including the thickness of the nickel strips being welded and the type of spot welder used.
Typically, a current of around 1000 to 1500 amps is required to create a strong weld for 18650 battery packs. The spot welder must be capable of delivering this current in short pulses to prevent overheating the battery cells. Overheating can damage the cells and reduce their lifespan, making it essential to use a welder with precise control over the welding process.
Characteristics of Spot Welding
Spot welding has several distinctive characteristics that make it stand out from other welding processes:
- Speed: Spot welding is incredibly fast, with each weld taking only a fraction of a second. This makes it ideal for high-volume production environments.
- Localised Heat: The heat generated is confined to a small area, reducing the risk of warping or damaging the surrounding material.
- No Filler Material Required: Unlike other welding techniques, spot welding does not require additional materials like filler rods or flux, making it a cost-effective process.
- Automatability:Spot welding can be easily automated, making it a common choice in industries where robots and automated systems are used for large-scale production.
- Strength:Spot welds are generally strong and durable, making them suitable for structural applications.
Where is Spot Welding Used?
Spot welding is used in a variety of applications, particularly in industries where metal sheets need to be quickly and efficiently joined together. The automotive industry is one of the largest users of spot welding, where it is used to assemble car bodies by welding together various panels and structural components.
Spot welding is also used in the manufacturing of household appliances, electronics, and metal furniture. Its ability to create strong, clean welds without the need for additional materials makes it ideal for applications where aesthetics are important.
What Industries Use Spot Welding?
- Automotive Industry: Spot welding is crucial for assembling car bodies, doors, and hoods. Automated spot welding systems allow car manufacturers to produce vehicles efficiently while ensuring the structural integrity of the welds.
- Electronics Industry: Spot welding is used to connect metal contacts in battery cells, such as 18650 batteries, ensuring a reliable electrical connection while minimising heat transfer to sensitive components.
- Aerospace Industry: In aerospace, spot welding is used for joining thin metal sheets and components. The ability to create strong, lightweight joints is essential in this industry.
- Appliance Manufacturing: Manufacturers of household appliances use spot welding to assemble metal parts, ensuring durability and aesthetics.
- Metal Furniture Industry: The process is widely used in the creation of metal furniture, where clean and strong welds are necessary.
Final Notes
Spot welding is a highly efficient and versatile welding process that plays a crucial role in industries like automotive, electronics, aerospace, and manufacturing. Its ability to create strong, durable joints without the need for filler materials makes it a cost-effective solution for high-volume production. While it is most commonly associated with steel, spot welding can be used with other metals, including aluminium, brass, and copper, although each material presents unique challenges.
Understanding the materials and equipment used, as well as the technical requirements, is essential to achieving successful spot welds in any application.
Get insights on industry news and posts.
Related Posts
April 17, 2025
Types of Welding and What are They Used For?
Welding is a foundational process in modern manufacturing, fabrication and…
February 25, 2025
What is Fusion Welding | Types and Processes
Fusion welding, also known simply as metal welding, is a process where two or…
October 1, 2024
How to MIG Weld
MIG welding is one of the most versatile and user-friendly welding processes,…